Generally we know about interfacing button switches, LED with Atmega32 microcontroller. We know that interface switch’s to one port, LED’s to another port and if we press any switch the corresponding LED will glow. But all the LED’s operate with single switch we don’t know.
Here we are developing the program for operating 7 LED’s with one switch. The circuit connections and programming is so simple. We will discuss here about that. First we see the circuit connections. Let us take any one port of Atemga32 controller is PortD. Connect 7 LED’s to PortD and connect on switch to remaining pin of the PortD as shown in circuit diagram.
Now let us start the coding for microcontroller. First open the Atmel Studio software of any version. Create a new project with your desired file name. Here I am taking the project name as “button switch”. In the text window type the program mentioned below and we will discuss each step clearly.
#include<avr/io.h>
#include<util/delay.h>
These are the header files for Atmega32 microcontroller main function and delay function.
void pressedbutton (int a);
void releasedbutton (int b);
This is the prototype declarations for the code blocks. These are mentioned at the beginning of the program. One is for button pressed and another is for button released. Next thing ‘a’ and ‘b’ are the two integer values. We don’t know which button is pressed, so ‘a’ stores the button pressed value and as same like ‘b’ also. We don’t know which button is released, so ‘b’ reads the released button status.
int pressed_level[1];
int released_level[1];
int pressed[1];
int lednumber[1];
This is the declaration of the global variables. The variables are represented in arrays because number represents the capacity of the array. If we want to increase the buttons the array size may change according to our requirements. For example we need to add two buttons for two ports and operating the 14 LED’s we need to replace 1 with 2. Here ‘pressed’ is the global variable to store the status of pressed button. Declaring the new variable as lednumber which can represents which LED is in on position.
Next about main function, we will have much aware about main function right..., next port initialization. Here we are taking PORTD among form the four ports. In PORTD from pin0 to pin6 we are declaring as outputs because we are interfacing LED’s to these pins only and pin7 is declaring as input because the button is connected to this pin only.
DDRD = 0b01111111;
PORTD = 0b10000000;
The above statements represent the port initialisation ‘0b’ means representing in binary values. Instead of ‘0b01111111’ we can represent with 0X7F also. The only difference is number format ‘01111111’ represents the binary value and ‘0X7F’ represents the hexadecimal value. In data direction register ‘0’ represents the input and ‘1’ represents the output. So in PORTD 7th declared as input and ‘0 to 6th’ pin declared as outputs and by using the PORT register all the pins ‘0 to 6’ make as output low and 7th pin as input high.
while (1)
{
}
This is loop condition that executes the condition infinite number of times.
The remaining only one thing in main function is button condition reading. We declared input pin is high in port declarations. One end of the button is connected to pin7 and another end of the button is connected to ground. At the pin side it has high value. If button is pressed that will connected to ground and the bit is cleared. That conditions we are mentioned under while loop with ‘if-else’ condition.
while(1)
{
If (bit_is_clear(PIND,7))
{
Pressedbutton(1);
}
else
{
releasedbutton(1);
}
}
In before we has declared the code blocks for pressed button and released button. In the above condition when ‘if’ condition is satisfied then there is a need to execute one code block. When ‘else’ condition is satisfied then there is a need to execute another code block. The prototype declaration of code blocks already mentioned in the program beginning.
void pressedbutton (int a)
{
pressed_level[a]++;
if (pressed_level[a] > 500)
{
if (pressed[a] == 0)
{
pressed[a] = 1;
if (a == 1)
PORTD |= 1 << lednumber[a];
lednumber[a] ++;
if (lednumber[a] > 7)
{
PORTD = 0b10000000;
lednumber[a] = 0;
}
}
pressed_level [a] = 0;
}
}
When we pressed the button, the value at the pin will become 0 and then of condition satisfied and pressedbutton code block will execute. We don’t know the button value, so pressed_level value will increment and that value is greater than 500, flow forward to next step. Here I mentioned the comparison value as 500 indicates the button pressed levels. When the pressed value is equal to zero, the pressed value becomes 1, when button pressed value is equal to 1; one LED in the PORTD and next increment the LED number according button pressed. When the led number reached the 7 then turn off the all LED’s and repeat from starting.
In the above section we discussed about pressed button code block. But in stating of the program we declared two code blocks one is for pressed button and another is for released button.
void releasedbutton (int b)
{
released_level [b] ++;
if (released_level [b] > 500)
{
pressed [b] = 0;
released_level [b] = 0;
}
}
Initializing the code block then we don’t know the released level of the button. So we are taking an array for storing the released button value. First increment the released level, then compare the condition for how many times the button was released and it is compared with 500. About that value we discussed in before. If the condition satisfied, pressed value is zero and released level is also zero.
Circuit:
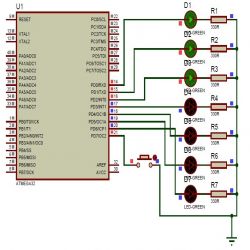
Code:
/*
* Button_LED.c
*
* Created: 15-07-2013 Prince 9:06:03
* Author: Vinnu
*/
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <util/delay.h>
void pressedbutton(int a); // code block declaration for pressed button
void releasedbutton(int b); // code block declaration for released button
int pressed_level[1]; // global values initialization for pressed level
int released_level[1]; // global values initialization for released level
int pressed[1]; // global values initialization to store which button is pressed
int lednumber[1]; // global values initialization for which led is on
int main(void)
{
DDRD = 0b01111111; // Port initialization
PORTD = 0b10000000; //pins enabling
while(1)
{
if (bit_is_clear (PIND, 7)) // bit is clear at pin7
{
pressedbutton(1); // code block will execute
}
else
{
releasedbutton(1); // other wise this code block will execute
}
}
}
void pressedbutton (int a)
{
pressed_level[a]++; // level increase one step
if (pressed_level[a] > 500) // conditional statement
{
if (pressed[a] == 0) // conditional statement
{
pressed[a] = 1; // pressed value is equal to 1
if (a == 1) // button pressed value is equal to 1
PORTD |= 1 << lednumber[a]; // one led will on
lednumber[a] ++; // led number will incremented
if (lednumber[a] > 7) // led number is grater than 7 repeat from starting
{
PORTD = 0b10000000;
lednumber[a] = 0;
}
}
pressed_level [a] = 0; // pressed level equal to zero
}
}
void releasedbutton (int b)
{
released_level [b] ++; // release level incremented
if (released_level [b] > 500) // button pressed level comparison
{
pressed [b] = 0; // pressed button is become zero
released_level [b] = 0; // released level is zero
}
}
Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét