Developed By:
Akshay Daga
The Self Programming Mode (SPM) is a feature which enables a microcontroller to program its own flash memory. Using the SPM a microcontroller can program itself with an SPM code. The SPM is commonly used with the microcontroller Boot-Loader codes which help to program the microcontroller serially. In AVR microcontroller the SPM is available only for the code running in the BLS of the flash memory. With the help of the SPM a code in BLS can rewrite the application flash memory entirely or a part of it. It can even rewrite its own code in the BLS section.
The SPM is a key factor of the Boot-Loader code since the major function of the Boot-Loader is to load an application code into the application flash section. The Boot-Loader may receive the code binary from other memory chips, SD-cards or through the serial port of the microcontroller in case of serial programming. It is then with the help of the SPM that the microcontroller write the binary code into the application flash section.
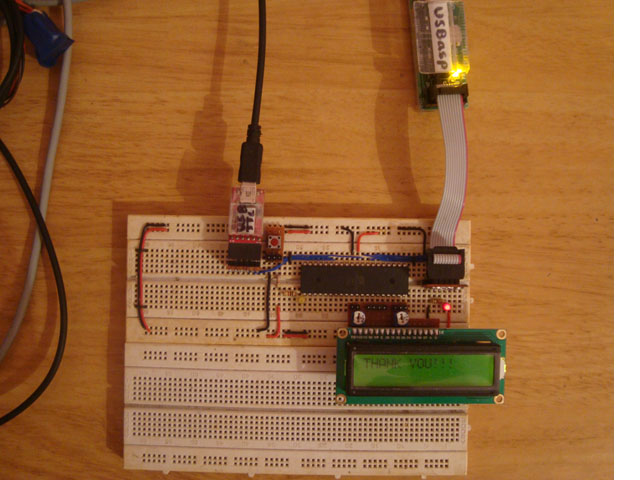
Self-Programming Mode (SPM) is a feature of the AVR microcontroller which enables the microcontroller to program its own flash memory. Only the code running on the BLS can make use of this SPM feature. The microcontroller can be made to start executing from the BLS from there the code can access the application flash area. The BLS can read or write the content of the entire flash including the BLS itself.

Fig. 2: Block Diagram of SPM with BLS in AVR
The task of writing the BLS code with SPM has been made simple by the APIs available in the header file <avr/boot.h>. The following are the important APIs available in the header file which helps in the SPM.
FUNCTION
|
DESCRIPTION
|
PARAMETER
|
boot_is_spm_interrupt ( )
|
Check if the SPM interrupt is enabled.
| |
boot_lock_bits_set (lock_bits)
|
Set the Boot-Loader lock bits
|
A mask of which Boot Loader Lock Bits to set
|
boot_lock_bits_set_safe (lock_bits)
|
Waits for EEPROM and SPM operations to complete before setting lock bits
|
A mask of which Boot Loader Lock Bits to set
|
boot_lock_fuse_bits_get (address)
|
Read the lock or fuse bits at the given address. Returns 0 or 1 according to the fuse bit is programmed or not
|
The address to be read
|
boot_page_erase (address)
|
Erase the flash page that is referred by address
|
A byte address in flash
|
boot_page_erase_safe (address)
|
waits for EEPROM and SPM operations to complete before erasing the page
|
A byte address in flash
|
boot_page_fill (address, data)
|
Fill the Boot-Loader temporary page buffer for flash address with data word
|
The address is a byte address. The data is a word
|
boot_page_fill_safe (address, data)
|
waits for EEPROM and SPM operations to complete before filling the page
|
The address is a byte address. The data is a word
|
boot_page_write (address)
|
Write the Boot-Loader temporary page buffer to flash page that contains address
|
Byte address in flash
|
boot_page_write_safe (address)
|
waits for EEPROM and SPM operations to complete before writing the page
|
Byte address in flash
|
boot_rww_busy ( )
|
Check if the RWW section is busy
| |
boot_rww_enable ( )
|
Enable the Read-While-Write memory section.
| |
boot_rww_enable_safe ( )
|
waits for EEPROM and SPM operations to complete before enabling the RWW memory
| |
boot_signature_byte_get (address)
|
Returns the Signature Row byte at the given address
|
Parameter address can be 0 to 0x1F
|
boot_spm_busy ( )
|
Check if the SPM instruction is busy
| |
boot_spm_busy_wait ( )
|
Wait while the SPM instruction is busy
| |
boot_spm_interrupt_disable ( )
|
Disable the SPM interrupt
| |
boot_spm_interrupt_enable ( )
|
Enable the SPM interrupt
|
Fig. 3: Important APIs in AVR's header file for SPM
Using the above APIs one can write a code for SPM in an AVR microcontroller provided that the code should follow certain steps in the order. In this project code which has been programmed from the beginning of the flash memory is re-programmed into another region of the flash memory as such. The task of programming one region of flash memory with the binary taken from the other region can be done in the following three major steps.
Step: 1 Erase the flash page which is about to write into
The first step is to erase the flash page which is about to be written with the new values. The API which helps in executing this step is;
Boot_page_erase (address)

Fig. 4: Figure represents Status of temporary page buffer and flash memory in SPM of AVR
Step: 2 Store the values in a temporary buffer before write into a flash page
This is the second step in which one should store the required binary in a temporary buffer, before writing to any of the flash memory page. The API that can be used for this purpose is;
boot_page_fill (address, data)
This API fills the Boot-Loader temporary page buffer byte by byte before flashing the data in the temporary page buffer into a page as such. The parameter data represents each byte in the buffer and the parameter address represents the page address + offset of the buffer location where the data byte need to be stored.
The following figure represents the operation in which the temporary page buffer is filled byte by byte using the API boot_page_fill (address, data).
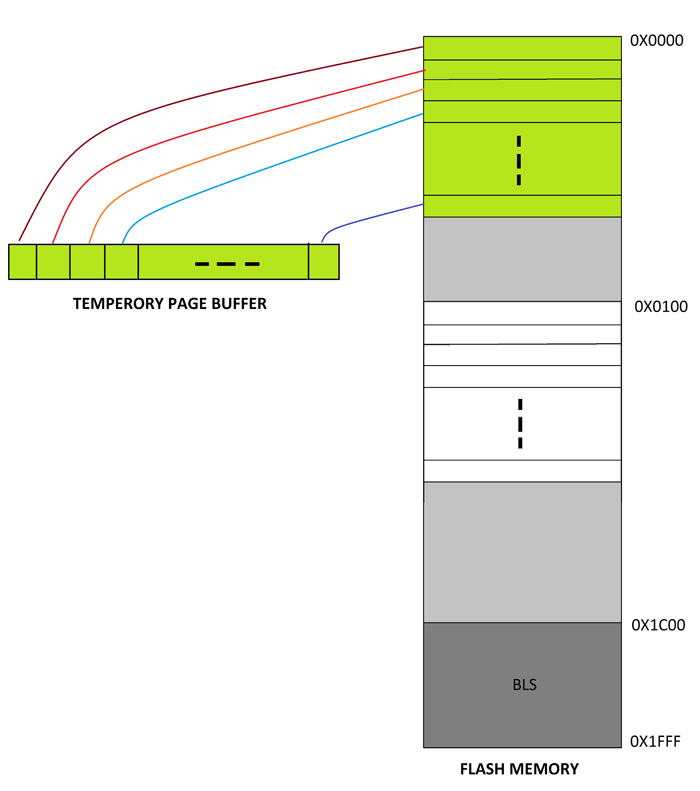
Fig. 5: Operation of Data Transfer to temporary page buffer using AVR's API boot_page_fill
The parameter data in the API boot_page_fill (address, data) is actually read from the first location of the flash memory itself with the help of another API which is available in the header file <avr/pgmspace.h>.
pgm_read_byte (address)
FUNCTION
|
DESCRIPTION
|
PARAMETER
|
pgm_read_byte (address)
|
This function returns the byte which it reads from the flash memory referred by the parameter ‘address’
|
Refers the location of the flash memory from which the byte need to be read
|
Step: 3 Program the filled temporary buffer into the already erased flash page
This is the final step in which the filled temporary buffer is flashed using an API into already erased page of the flash memory. The API which helps in this step is;
boot_page_write (address)
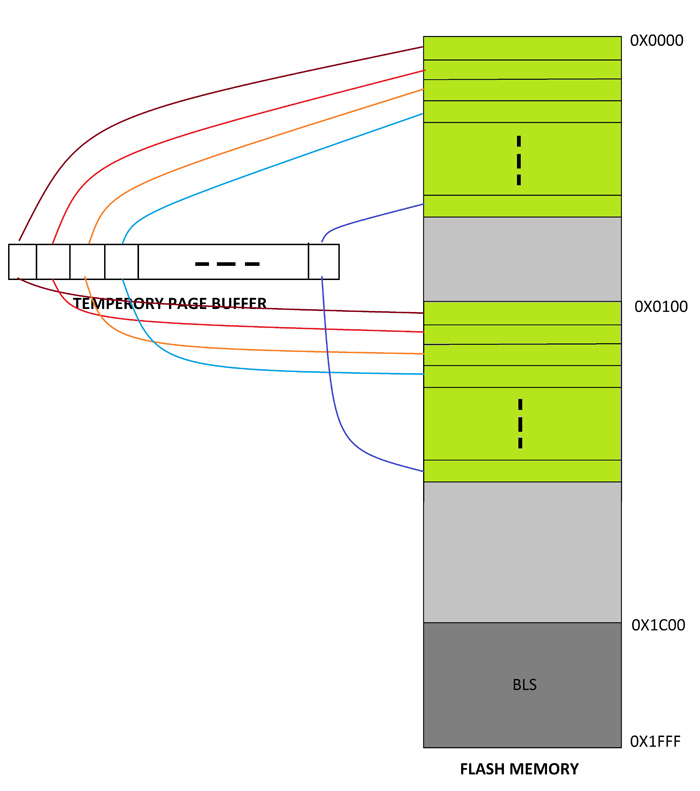
Fig. 6: Temporary Buffer Data transferred in AVR's Flash Memory using API
The code in this project which is written for the BLS can copy 300bytes from the flash memory into the temporary buffer starting from the address 0x0000. These bytes are then flashed into the flash memory page starting from the address 0x0100. After doing this the code from the BLS will make a jump to the address 0x0100 so that the re-written binary can be executed next. With this boot loader code, whatever program we flash into the address starting from 0x0000 will get rewritten at ox 0x0100 and executed. A simple LED blinking test application can be written into the flash memory starting from 0x0000 to test the working.
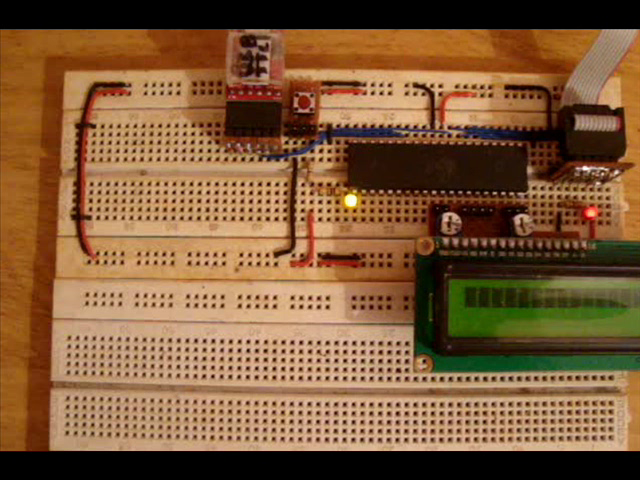
Fig. 7: LED Blinking using SPM of AVR circuit set up on breadboard
Circuit:

Code:
Code 2:
Không có nhận xét nào:
Đăng nhận xét